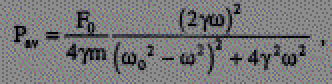
In this work we carry out mathematical formulation of the average power dissipation of a damped harmonic oscillator under the influence of a periodic driving force. We set up the equation of motion of a mass m, according to the second law of Newton, tied to a spring moving under the simultaneous action of the air resistance and a periodic force. It leads to a inhomogeneous second order linear differential equation. We solve the equation rigorously. Regulating the parameters, we can make that the homogeneous part of the solution to dampen rapidly. We then calculate the average power of the system over the period of the driving force.
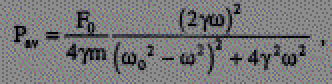
where w0 is the intrinsic angular frequency of the spring, w is the angular frequency of the driving force, gamma is the dampening parameter, and F0 is the magnitude of the driving force. We finally develop a Mathematica program to plot a three dimensional diagram of the average power depending on w and gamma. We explicitly demonstrate how the power increases as the driving frequency approaches the resonating frequency of the spring.